Température de fonctionnement des LED et de leur pilote – éclairage public électrique
Température de fonctionnement des LED et de leur pilote – éclairage public électrique
Introduction
De manière générale, les lampes LED génèrent une certaine chaleur lorsqu’elles fonctionnent, mais comparées aux sources lumineuses traditionnelles (comme les lampes à incandescence), elles dégagent généralement moins de chaleur. Cependant, les lampes LED doivent impérativement fonctionner dans une plage de températures raisonnable. Si la température de fonctionnement des LED prévue est dépassée, la lampe risque de mal fonctionner, voire d’être endommagée par la surchauffe. La température des lampes LED est influencée par de nombreux facteurs, notamment leur puissance, les performances de leur alimentation, la conception du système de dissipation thermique, la température ambiante et la durée de fonctionnement. Plus la puissance des puces LED est élevée, plus les performances de l’alimentation sont faibles, plus le système de dissipation thermique est mal conçu, plus la température ambiante est élevée et plus la durée de fonctionnement est longue, plus la température de la lampe risque d’augmenter. Ceci a forcément un impact négatif sur les principaux composants de la lampe (tels que les LED et l’alimentation) et peut, à terme, entraîner une panne d’éclairage public. Afin de garantir un fonctionnement stable et durable des lampes LED, les concepteurs privilégient une conception optimisée, incluant la structure, le circuit et la dissipation thermique, pour contrôler la température des puces LED et de l’alimentation et éviter toute surchauffe. Ci-dessous, la caméra thermique du fusil ZGSM et des éclairage public électrique de la série H.
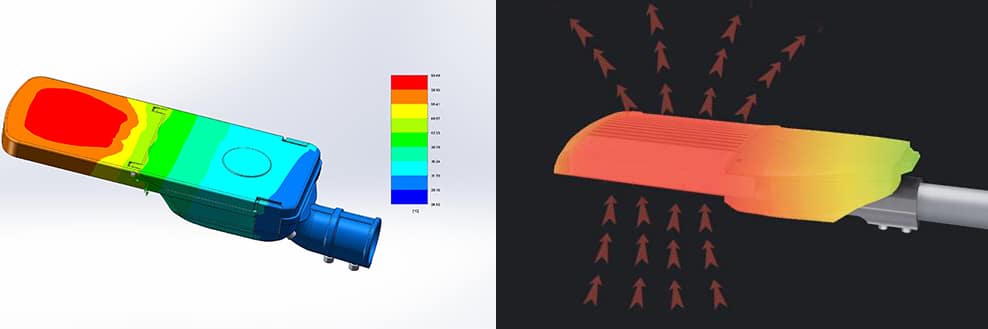
Pourquoi devrions-nous nous soucier de la température ?
La température des lampes LED dépend de nombreux facteurs, tels que la température de fonctionnement des LED et de l’alimentation, la température du boîtier, la température ambiante et les conditions d’utilisation. Les concepteurs doivent tenir compte de ces facteurs pour garantir un fonctionnement sûr des lampes LED et une bonne dissipation thermique, assurant ainsi un fonctionnement stable et durable et prévenant les pannes d’éclairage public.
- Une température excessive accentue la dégradation lumineuse des puces LED. Le rapport LM80 concernant la LED montre que plus la température est élevée, plus la durée de vie L70 est courte, c’est-à-dire que l’atténuation lumineuse est importante.
- Une température excessive augmente le taux de défaillance des puces LED. Des études ont montré qu’une chaleur excessive peut engendrer des contraintes thermiques sur les composants LED (tels que les joints de soudure et les circuits imprimés), provoquant ainsi une défaillance et endommageant l’ensemble du module.
- Une température excessive augmente le taux de défaillance des alimentations LED. Les spécifications de ces alimentations indiquent que le MTBF (temps moyen entre les pannes) diminue avec l’augmentation de la température.
- Plus la température ambiante de la lampe est basse lors de sa conception, plus son efficacité risque d’être compromise en environnements extrêmes. Par exemple, dans certains pays du Moyen-Orient, la température ambiante peut dépasser 40 degrés. Il est donc essentiel d’en tenir compte lors de la conception des luminaires.
Température de fonctionnement des LED
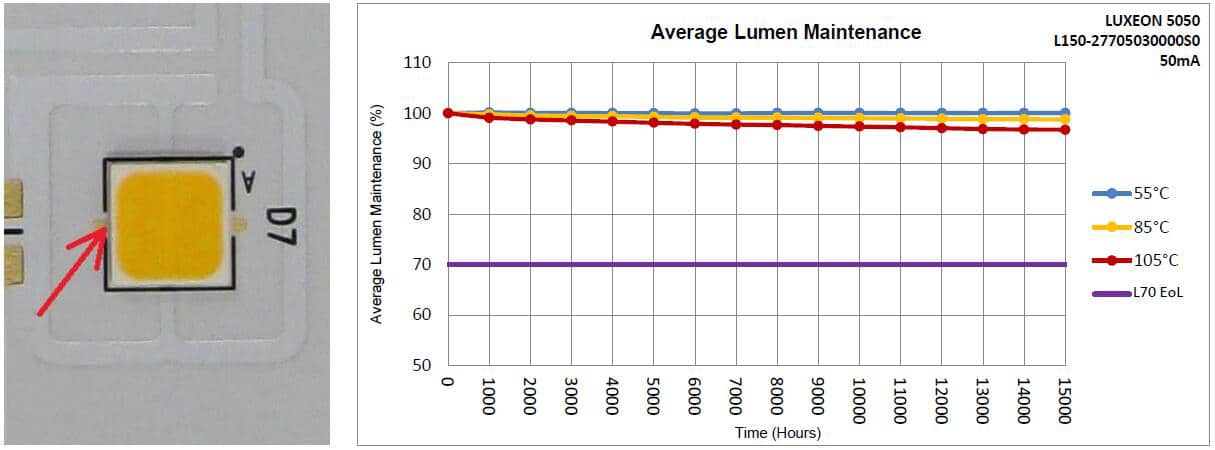
Les puces LED convertissent principalement l’énergie électrique en énergie lumineuse. Au cours de ce processus, une partie de l’énergie électrique est convertie en chaleur. Les puces LED génèrent donc progressivement de la chaleur et leur température augmente graduellement. Lorsque la chaleur produite par les LED et la chaleur dissipée s’équilibrent, la température se stabilise. Si la température reste dans la plage de température de fonctionnement nominale de la LED, celle-ci fonctionne normalement. Cependant, dans cette plage, plus la température est élevée, plus l’atténuation de la lumière (c’est-à-dire la diminution du flux lumineux) est importante. Il est donc nécessaire de prendre des mesures de conception et de dissipation thermique appropriées pour contrôler la température des LED et ainsi garantir leur durée de vie et leurs performances. Généralement, la plage de température de fonctionnement nominale des LED se situe entre -40 et 105 °C. Si la température dépasse 105 °C, les LED risquent d’être endommagées. La figure ci-dessous illustre l’atténuation de la lumière des LED en fonction de la température.
Température de fonctionnement du pilote LED
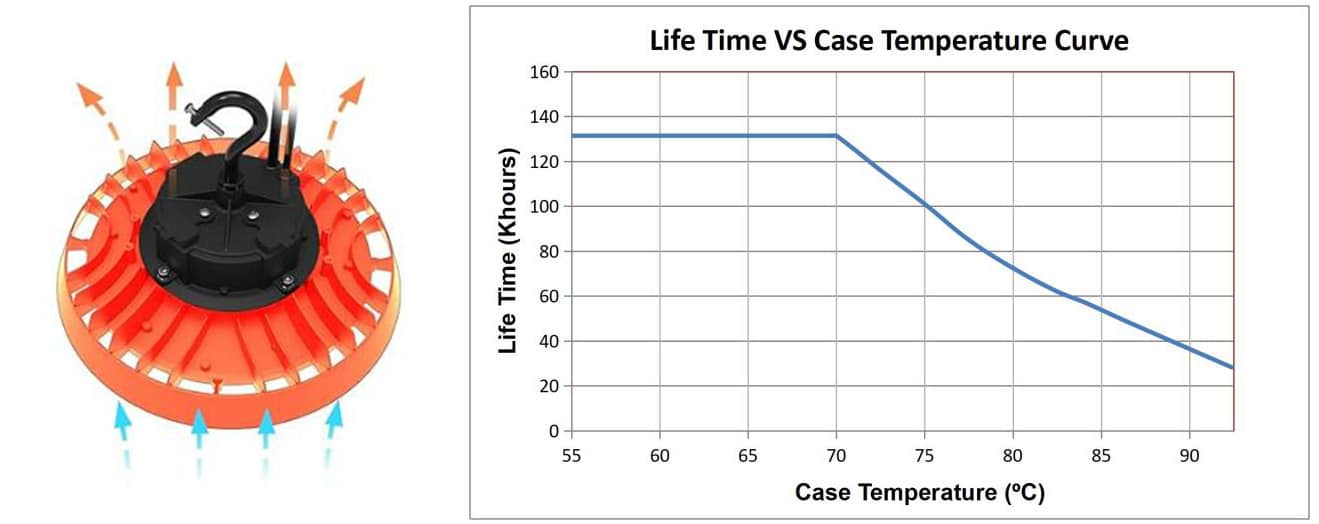
Composant essentiel des lampes LED, l’alimentation LED a pour fonction principale de convertir le courant alternatif en courant continu afin de fournir l’énergie électrique nécessaire au fonctionnement des puces LED. Lors de cette conversion, divers composants de l’alimentation consomment de l’énergie électrique, dont une partie est convertie en chaleur et dissipée. En général, la température de fonctionnement des alimentations LED reste modérée. Cependant, dans certaines conditions, comme une température ambiante élevée ou une proximité excessive entre le radiateur de la LED et l’alimentation, la température de cette dernière peut augmenter et son fonctionnement peut être altéré. La température de fonctionnement optimale d’une alimentation LED se situe généralement autour de 60 °C. À cette température, sa durée de vie est maximale. La température de fonctionnement nominale des alimentations LED est généralement comprise entre -40 °C et 80 °C. Au-delà de 80 °C, l’alimentation risque d’être endommagée. La figure ci-dessous illustre la courbe de durée de vie d’une alimentation LED en fonction de la température.
Température de fonctionnement des lampes LED (relation entre les LED, l’alimentation des LED et les lampes LED)
La température de fonctionnement des lampes LED est un facteur essentiel pour garantir leur fonctionnement stable et leurs performances à long terme. Lors de la conception de lampes LED, il est impératif de prendre en compte les températures de fonctionnement de la puce LED, de l’alimentation et du boîtier, ainsi que la température ambiante. Par exemple, si la température de fonctionnement maximale nominale d’une lampe est de 50 °C, tout dépassement de cette température augmente le risque d’endommager la lampe (y compris l’alimentation et les LED). Comment cette température est-elle déterminée ? Le ZGSM (Zero Gas Standard Management) est principalement déterminé en se référant aux performances des lampes LED (éclairage public et projecteurs) et des alimentations à différentes températures. Par exemple, à 50 °C, la température du point Ts (température de seuil) de la lampe LED est de 85 °C. On peut en déduire que la température du point Tj (température de jonction) est proche de 100 °C. Cette température étant proche de la température de fonctionnement maximale recommandée par le fabricant des LED, 50 °C est confirmée comme température de fonctionnement maximale de la lampe. Il est facile de comprendre que lorsque la température ambiante dépasse 50 °C, la température des principaux composants de la lampe (tels que les LED et l’alimentation) augmente encore. Bien que cela puisse avoir peu d’impact sur les lampes à court terme, un fonctionnement prolongé à haute température entraînera inévitablement le vieillissement et la détérioration des composants (Lampadaire LED avec thermistance NTC et protection contre la surchauffe).
Avantages de la séparation des cavités pour les LED et le pilote de LED des éclairage public électrique
ZGSM estime que la séparation de la cavité d’émission de lumière et de la cavité d’alimentation dans les lampes LED présente de nombreux avantages, le plus important étant la réduction des échanges thermiques entre les puces LED et l’alimentation. La chaleur générée par les puces LED n’est pas transmise à l’alimentation, évitant ainsi que celle-ci ne dépasse sa température de fonctionnement maximale et ne s’arrête. Les alimentations LED étant généralement dotées d’une protection contre la surchauffe, elles coupent automatiquement l’alimentation dès que la température dépasse un certain seuil. De même, la chaleur générée par l’alimentation n’est pas transmise aux puces LED, ce qui leur permet de dissiper la chaleur à temps, d’accélérer la dégradation de leur luminosité et d’endommager les puces. Il est donc essentiel de maintenir une distance suffisante entre la source lumineuse LED et l’alimentation pour éviter toute interférence thermique. La séparation de la cavité d’émission de lumière et de la cavité d’alimentation présente également d’autres avantages. Vous trouverez ci-dessous la conception de notre lampadaire électrique Falcon avec cavités séparées.
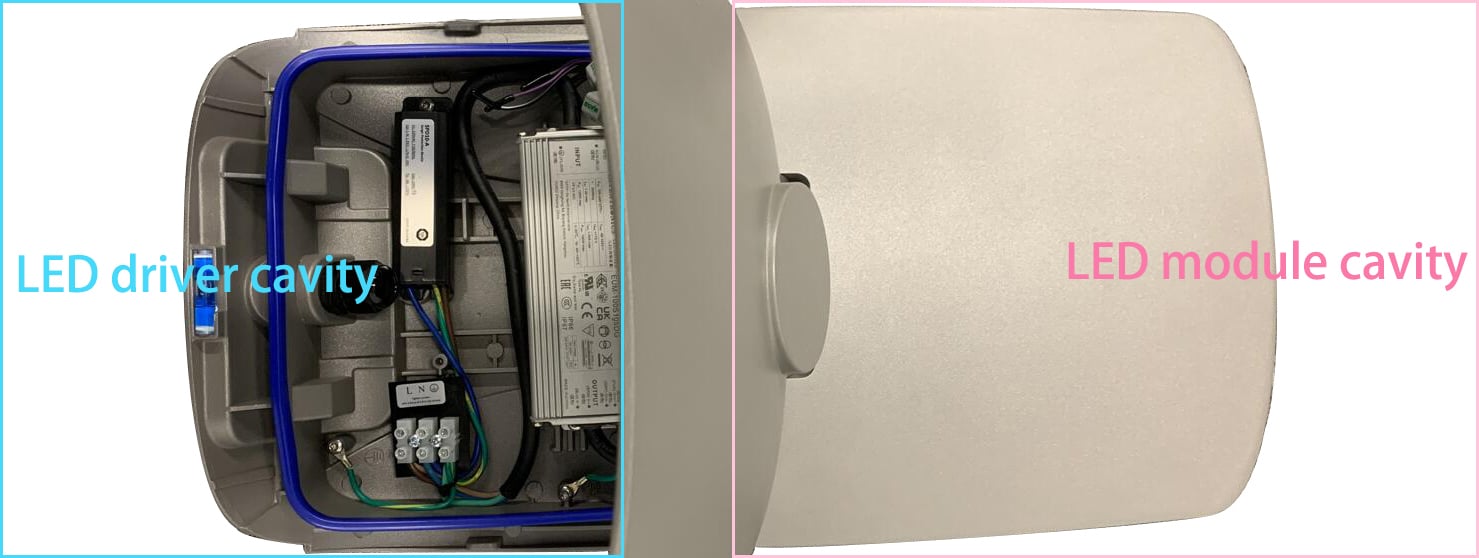

Maintenance et remplacement simplifiés : La conception compartimentée facilite la maintenance et le remplacement des lampes LED. En cas de panne de l’alimentation LED, il suffit d’ouvrir le compartiment d’alimentation pour la remplacer. Cette opération ne nécessite pas le démontage du module d’émission de lumière, ce qui simplifie la maintenance et évite tout impact potentiel du démontage sur les performances de la lampe (étanchéité, nettoyage de la lentille, etc.). Il en va de même pour le remplacement des puces LED, bien que les LED tombent rarement en panne.
Amélioration de la flexibilité de conception : La séparation de la cavité d’émission de lumière et de la cavité d’alimentation offre une plus grande flexibilité de conception. Pour la cavité d’émission de lumière, il suffit de prendre en compte la conception structurelle et l’installation des composants de l’unité d’émission. Pour la cavité d’alimentation, il suffit de considérer la conception structurelle et l’installation des composants de l’alimentation, de la protection contre les surtensions et du socle. Grâce à cette séparation, les fabricants peuvent concevoir des lampes de plus forte puissance dans des boîtiers plus compacts ou intégrer davantage de fonctionnalités tout en conservant les mêmes performances.
Lumières LED ZGSM
Les produits ZGSM sont soumis à des tests de température. Nous en tiendrons compte dès les premières étapes de la conception de l’éclairage. Une fois le modèle réalisé, nous testerons la température de l’ensemble des puces LED (Ts) et celle de l’alimentation LED (Tc) afin d’évaluer la pertinence de la conception. Après la finalisation de la conception, nous confierons à un organisme tiers la réalisation du test ISTMT, qui donne lieu à un rapport sur les températures Ts et Tc. Nous proposons également d’autres rapports, notamment LM82, LM84 et TM21, relatifs à la température du luminaire. Voici la gamme de produits ZGSM (lampadaires électriques, luminaires sur poteau, projecteurs, luminaires de marquise et luminaires sur mât d’éclairage) ; n’hésitez pas à nous contacter pour toute demande.
Résumé
Comme indiqué dans les sections précédentes, les puces LED et les alimentations fonctionnent correctement dans une plage de températures appropriée. Par conséquent, lors de la conception d’une lampe, il est essentiel de prendre en compte son environnement d’utilisation afin de garantir que la température ne dépasse pas la limite spécifiée. La température de fonctionnement des LED et de l’alimentation influe directement sur les performances globales et la durée de vie des lampes LED. Une gestion efficace de la température est cruciale pour la stabilité et la fiabilité à long terme des systèmes LED. Le rapport ISTMT relatif à l’éclairage public électrique fournit les données de température Ts de la puce LED et Tc de l’alimentation. ZGSM évalue les performances du système LED à partir de ces données et, si nécessaire, ajuste le courant de commande des LED, la structure de la lampe et l’alimentation. Il est également important de veiller à ce que la cavité d’émission de lumière et la cavité d’alimentation de la lampe LED soient aussi indépendantes que possible. Ceci permet d’éviter l’interaction thermique entre l’alimentation et les puces LED, prolongeant ainsi la durée de vie de chaque composant. Pour plus d’informations, n’hésitez pas à contacter ZGSM.
Rated Products
Related Blogs
Related Cases
People also ask
Author introduction

Hello Customers,
My name is Taylor Gong, I’m the product manager of ZGSM Tech. I have been in the LED lights industry for more than 13 years. Good at lighting design, street light system configuration, and bidding technology support. Feel free to contact us. I’m happy to provide you with the best service and products.
Email: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +8615068758483